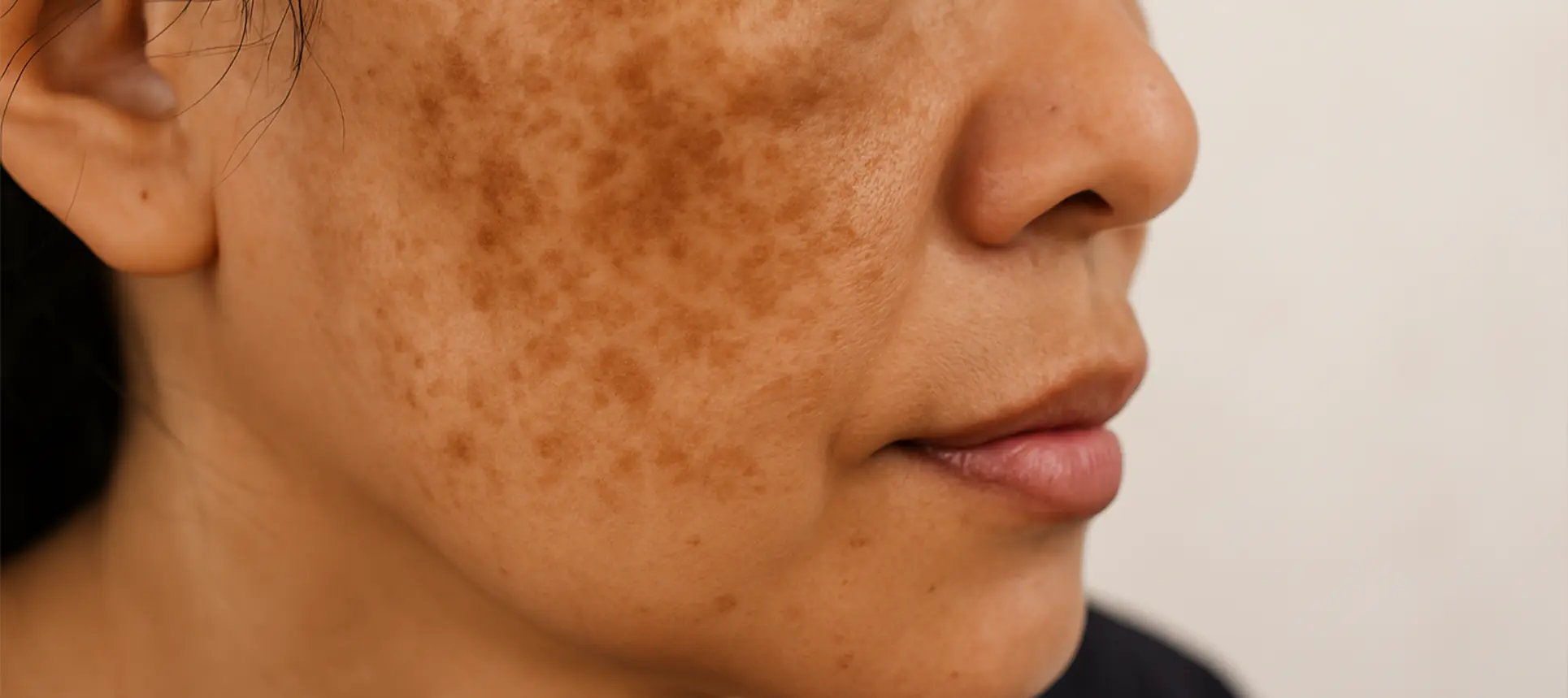
Hyperpigmentation is one of the most common—and often one of the most stubborn—skin concerns people face. Whether caused by sun exposure, acne, hormonal changes, or inflammation, hyperpigmentation can make the skin appear uneven, dull, or patchy. While it’s harmless, many people want to reduce its appearance to achieve a more radiant, balanced complexion. The good news is that with the right combination of treatments, ingredients, and habits, hyperpigmentation can be significantly improved over time.
Before beginning treatment, it’s essential to understand what type of hyperpigmentation you’re dealing with. Different causes respond to different treatments, and choosing the wrong approach can slow progress or even make pigmentation worse. With patience and the right strategies, however, noticeable improvement is absolutely possible.
1. What Causes Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation occurs when melanocytes—the cells responsible for producing pigment—overproduce melanin in certain areas. This buildup leads to darker patches or spots.
Common types include:
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH):
Dark marks left behind after acne, eczema, or injury.
Sunspots (solar lentigines):
Caused by cumulative sun exposure, often appearing on the face, chest, and hands.
Melasma:
Triggered by hormonal changes, often during pregnancy or with hormonal medication. Appears as symmetrical patches on the cheeks, upper lip, or forehead.
Freckles:
Genetic but darken with sun exposure.
Identifying the correct type helps you choose the most effective treatment plan.
2. Daily Sunscreen: The Non-Negotiable Essential
No matter the cause of hyperpigmentation, sunscreen is the absolute foundation of treatment. UV exposure worsens dark spots, triggers inflammation, and reactivates melasma—even through clouds or windows.
Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, and reapply during prolonged outdoor exposure. Mineral formulas with zinc oxide are especially good for those dealing with melasma or sensitivity.
Without sunscreen, even the best brightening serums will struggle to make progress.
3. The Most Effective Ingredients for Hyperpigmentation
There are several well-studied ingredients known to lighten dark spots safely and effectively.
Vitamin C
A powerful antioxidant that brightens and protects. Helps fade pigmentation and even skin tone.
Niacinamide
Reduces inflammation and slows melanin transfer to skin cells.
Azelaic Acid
Versatile and gentle—effective for acne marks, pigmentation, and redness.
Retinoids (retinol, adapalene, tretinoin)
Speed up cell turnover, fade dark marks, and boost collagen.
Alpha-Arbutin
A gentle yet potent brightening ingredient that inhibits melanin production.
Tranexamic Acid
Particularly effective for melasma and stubborn pigmentation.
Exfoliating Acids (AHAs/BHAs)
Glycolic acid, lactic acid, and salicylic acid remove dull surface cells, improving overall tone.
Building a routine with complementary ingredients produces faster, more noticeable results.
4. How to Layer Ingredients for Best Results
A simple but effective brightening routine might look like:
Morning:
- Gentle cleanser
- Vitamin C serum
- Niacinamide or azelaic acid
- Moisturiser
- Sunscreen
Evening:
- Cleanser
- AHA or BHA exfoliant (2–3 times per week)
- Retinol or tranexamic acid serum
- Moisturiser
Consistency is far more important than intensity. Trying too many strong actives at once can cause irritation, which ironically creates more hyperpigmentation.
5. Professional Treatments That Make a Big Difference
If topical products don’t give you the results you want, professional treatments can accelerate progress.
Chemical Peels:
Glycolic, lactic, and salicylic peels improve pigmentation and texture.
Microneedling:
Stimulates collagen and helps fade acne scarring and PIH.
Laser Therapy:
Some lasers target pigmentation directly, but caution is essential—wrong settings can worsen melasma or cause rebound pigmentation, especially for deeper skin tones.
LED Light Therapy:
Red and near-infrared light support healing and reduce inflammation.
Always choose a trained, reputable professional—pigmentation treatments require expertise.
6. Important Considerations for Melasma
Melasma is complex and often hormonally driven, making it more resistant to treatment. Sunlight and heat can trigger flare-ups, even from sources like cooking or hot showers.
Effective melasma management includes:
- Daily sunscreen (SPF 50 if possible)
- Avoiding intense heat exposure
- Using soothing ingredients such as niacinamide
- Incorporating tranexamic acid
- Gentle, consistent treatment instead of aggressive exfoliation
Melasma rarely disappears completely, but it can be significantly controlled.
7. Habits That Help Prevent Pigmentation
Beyond products, several habits support long-term improvement:
- Wearing hats and sunglasses outdoors
- Avoiding picking or squeezing acne
- Moisturising regularly to support the skin barrier
- Using antioxidants daily
- Controlling inflammation and irritation
Healthy skin resists pigmentation more effectively.
8. Patience: The Most Overlooked Key to Success
Hyperpigmentation fades slowly because melanin sits deep within the skin. Most people see noticeable improvement after 6 to 12 weeks, with continued progress over time. Consistency is far more important than speed.
Final Thoughts
Hyperpigmentation can be frustrating, but it’s absolutely manageable with the right approach. By combining targeted ingredients, professional treatments when needed, and protective daily habits—especially sunscreen—you can dramatically improve uneven tone and achieve brighter, clearer skin. Progress may take time, but every step you take builds toward long-lasting results.